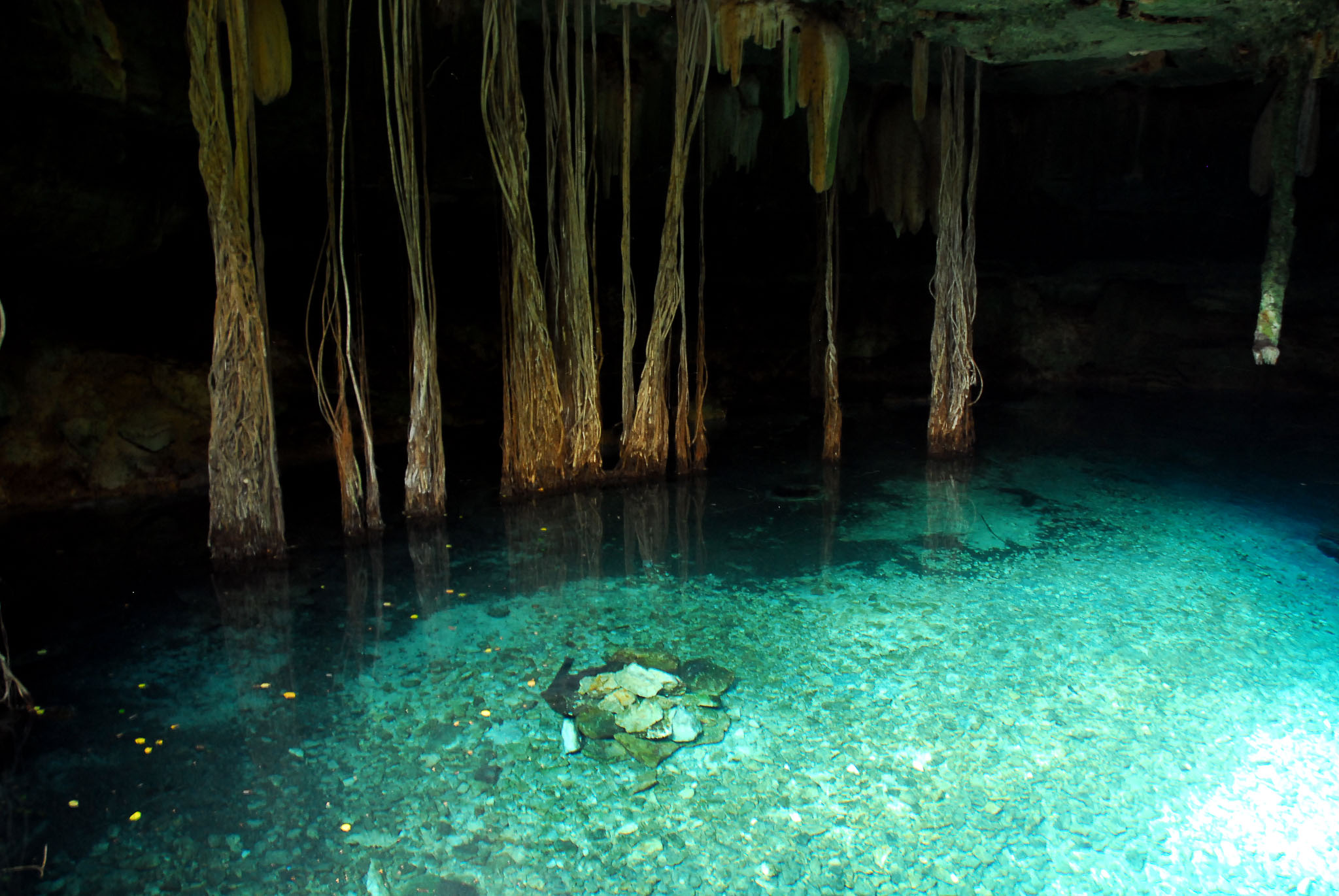
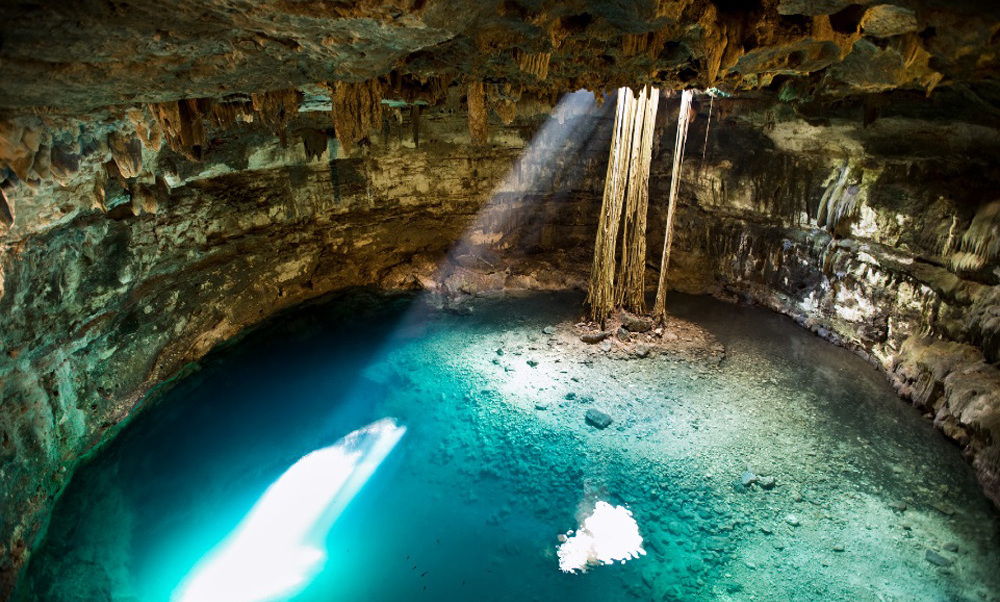
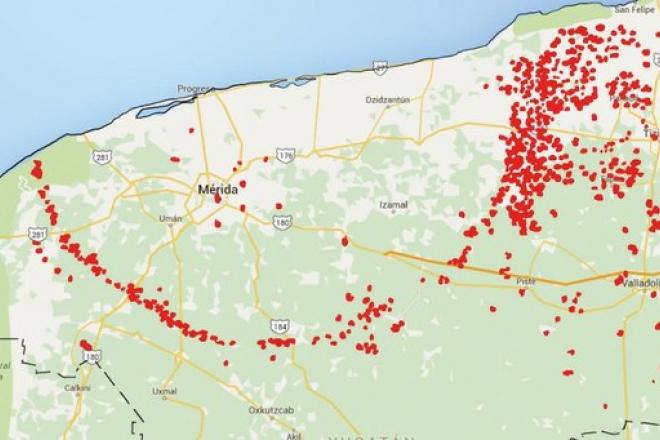
The cenotes ring is a circle that surrounds the collision point of the meteor that may have ended the era of the dinosaurs. Inside the ring are located Merida and the most important ports of Yucatan’s northern coast….
MERIDA — Authorities in Yucatan stepped up action before the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) so that the cenotes ring could be considered as a world heritage of mankind.
The ring of cenotes appeared 65 million years ago after the impact of a meteor in the area that now is the Port of Chicxulub, on the north coast of Yucatan.
Inside this underground system flows hundreds of water streams in what is considered one of the most important hydrological reserves of Mexico.
To make the request for the cenotes ring to be considered a natural heritage of mankind, three priority points were remarked:
- It is one of the most important water reserves in Mexico.
- Inside there live dozens of endemic species of flora and fauna.
- In 225 cenotes of Yucatan have been found Mayan vestiges, human remains and animal bones and fossils of more than 10 thousand years of antiquity.
In Yucatan state there are about 130 cenotes that make up the ring that is recognized by Unesco, although in the Yucatan Peninsula there are many more bodies of water of the same kind.
Jose Ruiz Silva, a member of Castic Systems of Yucatan, said that in the peninsula there are an estimated 8 thousand and 10 thousand cenotes, and just in Yucatan state there are 3 thousand.
It is expected that in 2018 Unesco make a resolution regarding whether to incorporate or not the ring of cenotes in the list of mankind’s heritage.
Source: noticieros.televisa.com